Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can significantly impact patent management by automating and optimizing various tasks. By leveraging AI and ML in these areas, patent management processes can become more efficient, accurate, and proactive, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of intellectual property management strategies. There are several applications and areas where AI/ML can be applied in patent management: Prior Art Search, Automated Patent Drafting, Patent Classification, Patent Valuation, Automated Patent Filing and Prosecution, Patent Portfolio Management, Patent Analytics, Infringement Detection, Technology Landscape Analysis, Patent Litigation Support, Automated Patent Maintenance and Collaborative Innovation Platforms.
E: Patent Filing and Prosecution
AI/ML technologies are transforming patent prosecution by automating routine tasks, providing valuable insights, and improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the process. Companies like Docket Alarm, InQuartik, and Legal Robot are at the forefront of integrating AI into patent prosecution workflows. AI/ML technologies are increasingly playing a role in the patent prosecution process, helping patent professionals streamline workflows, enhance efficiency, and make data-driven decisions. Patent prosecution involves interactions with patent offices, including the preparation, filing, and examination of patent applications:
Prior Art Search: AI-powered tools can conduct extensive prior art searches more efficiently than traditional methods. They analyze vast databases of existing patents, scientific literature, and other sources to identify relevant prior art. Saves time for patent examiners and attorneys, improving the quality and comprehensiveness of prior art searches. Claim Analysis and Drafting: AI/ML algorithms analyze patent claims, helping patent professionals draft claims that are more likely to be accepted by patent offices. They can suggest language based on successful claim patterns and examiner preferences. Improves the quality of patent applications, potentially reducing the number of rejections and enhancing the likelihood of successful prosecution.
Prosecution Analytics: Machine learning models analyze historical patent prosecution data to predict outcomes, estimate timelines, and identify potential challenges. They can provide insights into the strategies that have proven successful in the past.Helps patent professionals make informed decisions and strategize for efficient prosecution. Patent Examiner Interaction: AI tools analyze historical interactions with specific patent examiners, providing insights into their examination patterns, preferences, and tendencies. This information can inform communication strategies during prosecution. Enhances communication between patent professionals and examiners, potentially leading to smoother prosecution processes.
Automating patent filing and prosecution involves using AI/ML algorithms to streamline and optimize various tasks associated with the preparation, filing, and processing of patent applications. The combination of these AI/ML algorithms can contribute to the automation of various patent filing and prosecution tasks, reducing manual efforts, improving efficiency, and enhancing the overall quality of the patent prosecution process: Natural Language Processing (NLP): Analyzing and understanding the natural language used in patent documents, including applications and responses. Automated parsing and extraction of relevant information from patent documents. Improving the efficiency of drafting responses to office actions. Machine Translation: Translating patent documents between different languages. Facilitating the filing of international patent applications. Ensuring accurate translation of documents for patent prosecution in various jurisdictions. Predictive Analytics: Predicting outcomes or timelines in the patent prosecution process. Estimating the likelihood of success for a patent application. Predicting the time and resources required for prosecution. Classification Algorithms: Automatically categorizing patents into specific classes or subclasses. Streamlining the classification process during filing. Ensuring accurate categorization for efficient prosecution. Automated Patent Drafting: Generating patent application drafts with minimal human intervention. Speeding up the initial drafting process. Ensuring adherence to legal and formatting requirements.

Decision Trees: Assisting in decision-making during the prosecution process. Identifying optimal responses to office actions. Automating certain decisions based on predefined criteria. Image Recognition: Analyzing and extracting information from patent drawings and diagrams. Automated processing of visual elements in patent applications. Facilitating the understanding of visual components for examiners. Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Converting scanned or image-based patent documents into machine-readable text. Enabling the extraction of text information for analysis. Facilitating the search and retrieval of information from image-based documents. Reinforcement Learning: Training models to make sequential decisions during prosecution. Adaptive strategies for responding to office actions. Enhancing the decision-making process over multiple stages. Text Mining and Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing the content of patent-related communications. Assessing the sentiment and tone of examiner communications. Identifying potential challenges or issues in real-time. Semantic Search: Enhancing the accuracy of search functionalities within patent databases. Efficiently retrieving relevant prior art during the drafting and prosecution stages. Improving the accuracy of search results for examiners. Case-Based Reasoning: Leveraging past cases to make informed decisions. Drawing insights from historical patent prosecution cases. Guiding strategies based on successful precedents.
AI/ML accelerates various aspects of patent prosecution, reducing the time required for tasks such as prior art search, claim drafting, and data analysis.Data-driven insights from AI help patent professionals make informed decisions, optimize strategies, and increase the likelihood of successful prosecution. AI tools assist in drafting high-quality patent applications, leading to stronger claims and potentially reducing the likelihood of rejections. AI/ML provides strategic insights by analyzing historical data, helping patent professionals develop effective prosecution strategies. AI/ML technologies are transforming patent prosecution by automating routine tasks, providing valuable insights, and improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
Docket Alarm (now part of Fastcase) offers AI-driven analytics tools that assist in predicting litigation outcomes and analyzing patent prosecution data. Their platform aims to provide insights into the behavior of judges and examiners. Helps patent professionals make data-driven decisions during prosecution. InQuartik (Patentcloud) platform utilizes AI for prior art search, claim analysis, and patent portfolio management. The tools aim to streamline the patent prosecution process. Enables more efficient prosecution with advanced analytics and search capabilities. Legal Robot applies natural language processing and machine learning to analyze legal documents, including patents. The platform aims to assist patent professionals in drafting and prosecuting patents. Automates and enhances the analysis of legal documents, potentially improving efficiency in patent prosecution.
Docket Navigator: Docket Navigator provides litigation analytics and case tracking. While it is not exclusively focused on patent filing and prosecution, it incorporates AI for analyzing legal data, which may have applications in patent-related tasks. IPfolio: IPfolio is an Intellectual Property Management platform that includes tools for patent management. It leverages AI/ML for streamlining various IP processes, including patent filing and prosecution. Legal.io: Legal.io offers a platform for legal operations, and it may include features related to patent filing and prosecution automation. The platform uses AI to optimize legal workflows. Anaqua: Anaqua provides IP management solutions, and its platform includes features for automating patent prosecution tasks. It aims to enhance efficiency in managing the entire intellectual property lifecycle. Lecorpio (by Anaqua): Lecorpio, now part of Anaqua, offers an Intellectual Property Management platform with features for automating patent processes. This includes AI-driven tools for streamlining prosecution tasks.
Clarivate Analytics (IP Management Solutions): Clarivate Analytics offers IP management solutions, and its platform may incorporate AI for patent-related tasks, including filing and prosecution. The platform includes tools like IPfolio. Darts-ip: Darts-ip focuses on IP case law data and analytics. While its primary focus is on litigation data, the platform may integrate AI techniques for various IP-related tasks, including patent prosecution. Questel (Orbit Intelligence): Questel offers IP management and intelligence solutions, and its Orbit Intelligence platform may incorporate AI for patent filing and prosecution tasks. The platform provides analytics and workflow management. IFI CLAIMS Patent Services provides patent data solutions. While it may not be a direct patent filing platform, its data services may be used in combination with AI for various patent-related tasks. PatSnap: PatSnap is an IP intelligence platform that incorporates AI for various IP-related tasks. It may include features related to patent filing and prosecution automation.
Automating the patent filing and prosecution process using AI/ML can bring about several key benefits, and organizations often define objectives and key results (OKRs), key performance indicators (KPIs), and metrics to measure the impact and success of the automation efforts: Efficiency Improvement: Increase the efficiency of the patent filing and prosecution process. Reduction in the time taken for filing and prosecution tasks. Increase in the number of applications processed within a given timeframe. Cost Reduction: Achieve cost savings in the patent filing and prosecution workflow. Reduction in labor costs associated with manual tasks. Decrease in overall operational costs. Accuracy Enhancement: Improve the accuracy of patent filing and prosecution tasks. Reduction in errors or inaccuracies in filing documents. Increase in the accuracy of responses to office actions.
Resource Optimization: Optimize the utilization of human and computational resources. Improved resource allocation for different stages of the process. Reduction in idle time and bottlenecks in the workflow. Speed of Prosecution: Accelerate the prosecution of patent applications. Reduction in the time taken to receive a patent grant. Faster response times to office actions. Quality of Applications: Enhance the overall quality of patent applications. Increase in the number of granted patents. Improvement in the quality of drafted patent claims. Compliance and Consistency: Ensure compliance with legal and procedural requirements. Reduction in compliance errors in filed documents. Consistency in adhering to patent office guidelines. Risk Mitigation: Mitigate risks associated with patent prosecution. Reduction in the likelihood of rejections or objections. Decrease in legal challenges or disputes.
Workload Balancing: Achieve a balanced distribution of workload among team members. Even distribution of tasks among team members. Reduced backlog of tasks awaiting processing. User Satisfaction: Improve user satisfaction with the patent filing and prosecution process. Positive feedback from internal teams and external stakeholders. Improved user experience in interacting with automated systems. Adaptability to Changes: Ensure the system can adapt to changes in patent laws and regulations. Time taken to implement updates or changes in filing requirements. Accuracy in adapting to new legal or procedural changes. Search and Retrieval Efficiency: Enhance the efficiency of searching and retrieving relevant information. Reduction in time spent on prior art searches. Improvement in the precision and recall of search results.
E: Example
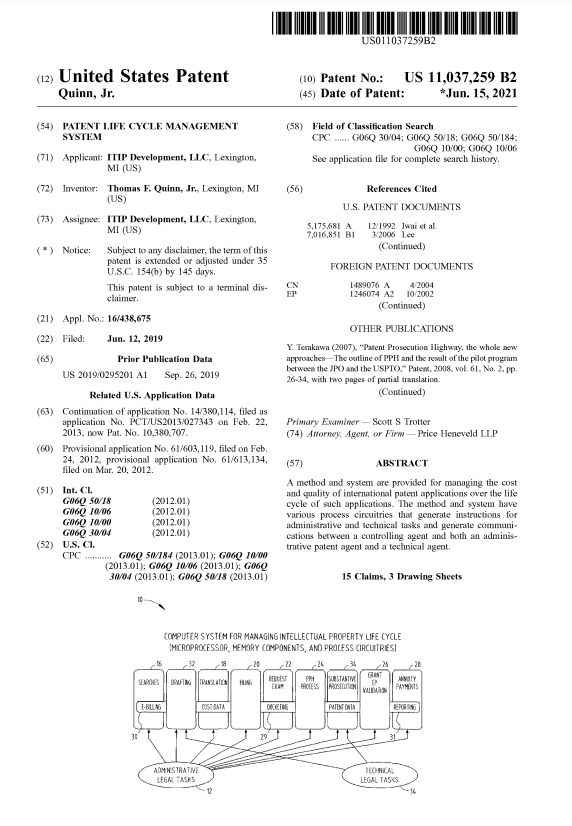
A system and approach are presented to oversee the expenses and quality of global patent applications throughout their lifecycle. This system involves diverse procedural components that produce directives for administrative and technical responsibilities and facilitate communication between a controlling agent and both an administrative patent agent and a technical agent.
In its most basic form, the current innovation is a method for managing the cost associated with obtaining international intellectual property (IP) protection. The method involves initially categorizing tasks involved in the process of obtaining international IP protection into administrative and technical, as depicted in FIG. 1. Subsequently, at least one of the administrative tasks is assigned to an administrative agent at a rate lower than that charged by the technical agent and, optionally, at a fixed flat fee. In one aspect of this innovation, administrative tasks encompass activities such as conducting a novelty search, translating a patent application, filing international patent applications, requesting examination, filing a request for grant under the PPH, correcting formalities, paying a grant fee, validating a granted application in multiple patent offices, proofreading the granted application, paying annuity fees, auditing charges for such tasks, and other miscellaneous administrative activities like recording assignments, filing declarations, docketing patent application data, processing invoice data, and similar tasks.
References
Automated Patent Filing and Prosecution:
Book: “Patent Prosecution: Practice and Procedure Before the U.S. Patent Office” by Laurence M. Kohn
Article: “The Role of AI in Patent Prosecution” by Susan K. McBee (Journal of Intellectual Property, 2019)
Webinar: “AI in Patent Prosecution: Promise or Peril?” by IPWatchdog
Course: “Patent Prosecution: A Practical Guide” on Practising Law Institute (PLI)
Blog Post: “How AI is Changing Patent Prosecution” by Patent Bots



